Server API JWKS auth
Centrifugo PRO supports protecting HTTP API and GRPC API with JWKS (JSON Web Key Set) based authentication. This allows you to use JWT tokens issued by your identity provider (like Keycloak, Auth0, or any other OIDC-compliant provider) to authenticate server API requests.
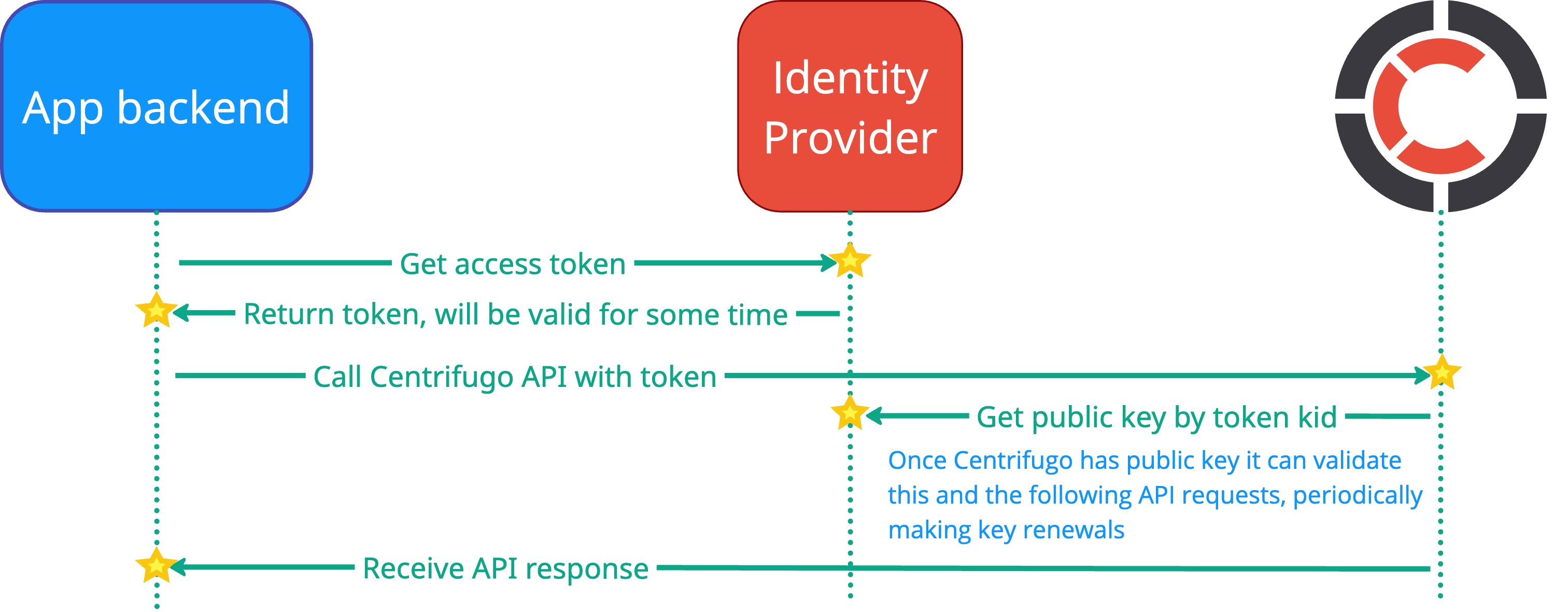
Overview
Instead of using the traditional API key authentication with X-API-Key header (for HTTP API) or metadata (for GRPC API), you can configure Centrifugo to validate JWT tokens signed by keys from a JWKS endpoint. This provides a more flexible and standardized way to protect your server API, especially when integrating with existing identity and access management systems.
The feature available since Centrifugo PRO v6.3.2
Configuration
HTTP API
JWKS authentication is configured under the http_api.jwks section:
{
"http_api": {
"jwks": {
"enabled": true,
"endpoint": "https://keycloak.test.env/auth/realms/myrealm/protocol/openid-connect/certs",
"audience": "https://centrifugo.test.env",
"issuer": "https://keycloak.test.env/auth/realms/myrealm",
"scope": "centrifugo:api"
}
}
}
GRPC API
JWKS authentication is configured under the grpc_api.jwks section:
{
"grpc_api": {
"enabled": true,
"port": 10000,
"key": "optional-api-key",
"jwks": {
"enabled": true,
"endpoint": "https://keycloak.example.com/.well-known/jwks.json",
"audience": "my-audience",
"issuer": "https://keycloak.example.com",
"scope": "centrifugo:api",
"tls": {
"enabled": true
}
}
}
}
Configuration options
http_api.jwks.enabled / grpc_api.jwks.enabled
Boolean. Default: false.
Turns on JWKS authentication for HTTP API or GRPC API. When enabled, Centrifugo will validate JWT tokens from the Authorization: Bearer <TOKEN> header (for HTTP API) or from gRPC metadata (for GRPC API) against the JWKS endpoint.
http_api.jwks.endpoint / grpc_api.jwks.endpoint
String. Required when JWKS is enabled.
URL to fetch JWKS from. This is typically the OIDC provider's JWKS endpoint.
Examples:
- Keycloak:
https://keycloak.example.com/realms/myrealm/protocol/openid-connect/certs - Auth0:
https://YOUR_DOMAIN.auth0.com/.well-known/jwks.json - Custom OIDC provider:
https://identity.example.com/.well-known/jwks.json
http_api.jwks.audience / grpc_api.jwks.audience
String. Optional, when not set audience check is skipped. It's recommended to set it.
The expected audience claim (aud) in the JWT token. This should match the audience configured in your identity provider for Centrifugo.
Example: https://centrifugo.test.env
http_api.jwks.issuer / grpc_api.jwks.issuer
String. Optional, when not set issuer check is skipped. It's recommended to set it.
The expected issuer claim (iss) in the JWT token. This should match the issuer of tokens from your identity provider.
Example: https://keycloak.test.env/auth/realms/myrealm
http_api.jwks.scope / grpc_api.jwks.scope
String. Optional.
The required scope claim in the JWT token. If set, Centrifugo will verify that the token contains this scope. The scope claim can be either a string or an array of strings in the JWT.
Example: centrifugo:api
http_api.jwks.tls / grpc_api.jwks.tls
Unified TLS object. Optional.
TLS configuration for HTTPS connection to JWKS endpoint. Use this if your JWKS endpoint requires custom TLS settings, such as custom CA certificates or client certificates.
Usage
HTTP API
Once JWKS authentication is configured, API clients need to provide a valid JWT token in the Authorization header when making HTTP API requests:
curl --header "Authorization: Bearer <JWT_TOKEN>" \
--request POST \
--data '{"channel": "chat", "data": {"text": "hello"}}' \
http://localhost:8000/api/publish
Example with httpie:
echo '{"channel": "chat", "data": {"text": "hello"}}' | \
http POST "http://localhost:8000/api/publish" \
"Authorization: Bearer <JWT_TOKEN>"
GRPC API
For GRPC API, clients need to provide the JWT token in the gRPC metadata with the authorization key:
authorization: Bearer <JWT_TOKEN>
The exact implementation depends on your gRPC client library. Here's an example using Go:
import (
"context"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"google.golang.org/grpc/metadata"
)
// Create context with authorization metadata
md := metadata.New(map[string]string{
"authorization": "Bearer " + token,
})
ctx := metadata.NewOutgoingContext(context.Background(), md)
// Make GRPC API call with authenticated context
response, err := client.Publish(ctx, &api.PublishRequest{
Channel: "chat",
Data: []byte(`{"text": "hello"}`),
})
JWKS caching, refresh and rotation
Centrifugo automatically caches the JWKS keys fetched from the endpoint to avoid making a request on every API call. The cache is periodically refreshed to pick up key rotations performed by your identity provider.
Combining with API key authentication
JWKS authentication can be used alongside API key authentication provided by Centrifugo OSS. If both http_api.key and http_api.jwks are configured (or grpc_api.key and grpc_api.jwks), Centrifugo PRO will accept requests authenticated with either method:
{
"http_api": {
"key": "my-api-key",
"jwks": {
"enabled": true,
"endpoint": "https://keycloak.test.env/auth/realms/myrealm/protocol/openid-connect/certs",
"audience": "https://centrifugo.test.env",
"issuer": "https://keycloak.test.env/auth/realms/myrealm"
}
},
"grpc_api": {
"enabled": true,
"port": 10000,
"key": "my-api-key",
"jwks": {
"enabled": true,
"endpoint": "https://keycloak.test.env/auth/realms/myrealm/protocol/openid-connect/certs",
"audience": "https://centrifugo.test.env",
"issuer": "https://keycloak.test.env/auth/realms/myrealm"
}
}
}
This can be useful during migration from API key to JWKS authentication, or when you need to support both authentication methods simultaneously.
Example: Keycloak integration
Here's a complete example of integrating Centrifugo HTTP API and GRPC API with Keycloak:
-
Configure Keycloak client:
- Create a client in Keycloak with client authentication enabled
- Set valid redirect URIs
- Add a custom scope
centrifugo:api - Note the JWKS endpoint URL from realm settings
-
Configure Centrifugo:
{
"http_api": {
"jwks": {
"enabled": true,
"endpoint": "https://keycloak.example.com/auth/realms/myrealm/protocol/openid-connect/certs",
"issuer": "https://keycloak.example.com/auth/realms/myrealm",
"scope": "centrifugo:api"
}
},
"grpc_api": {
"enabled": true,
"port": 10000,
"jwks": {
"enabled": true,
"endpoint": "https://keycloak.example.com/auth/realms/myrealm/protocol/openid-connect/certs",
"issuer": "https://keycloak.example.com/auth/realms/myrealm",
"scope": "centrifugo:api"
}
}
}
- Obtain a token from Keycloak (usually this is done by your backend service):
TOKEN=$(curl -X POST "https://keycloak.example.com/auth/realms/myrealm/protocol/openid-connect/token" \
-H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
-d "client_id=myclient" \
-d "client_secret=mysecret" \
-d "grant_type=client_credentials" \
-d "scope=centrifugo:api" \
| jq -r '.access_token')
- Use the token with Centrifugo HTTP API (usually this is done by your backend service):
curl --header "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" \
--request POST \
--data '{"channel": "chat", "data": {"text": "hello"}}' \
https://centrifugo.example.com/api/publish
- Use the token with Centrifugo GRPC API (usually this is done by your backend service):
md := metadata.New(map[string]string{
"authorization": "Bearer " + token,
})
ctx := metadata.NewOutgoingContext(context.Background(), md)
response, err := client.Publish(ctx, &api.PublishRequest{
Channel: "chat",
Data: []byte(`{"text": "hello"}`),
})