Push notification API
Centrifugo excels in delivering real-time in-app messages to online users. Sometimes though you need a way to engage offline users to come back to your app. Or trigger some update in the app while it's running in the background. That's where push notifications may be used. Push notifications delivered over battery-efficient platform-dependent transport.
With Centrifugo PRO push notifications may be delivered to all popular application platforms:
- Android devices
- iOS devices
- Web browsers which support Web Push API (Chrome, Firefox, see this matrix)
Centrifugo PRO provides API to manage user device tokens, device topic subscriptions and API to send push notifications towards registered devices and group of devices (subscribed to a topic). API also supports timezone-aware push notifications, push localizations, templating and per user device push rate limiting. You can also use your own device token storage and use Centrifugo PRO as a high-performance way to send push notifications to supported providers.
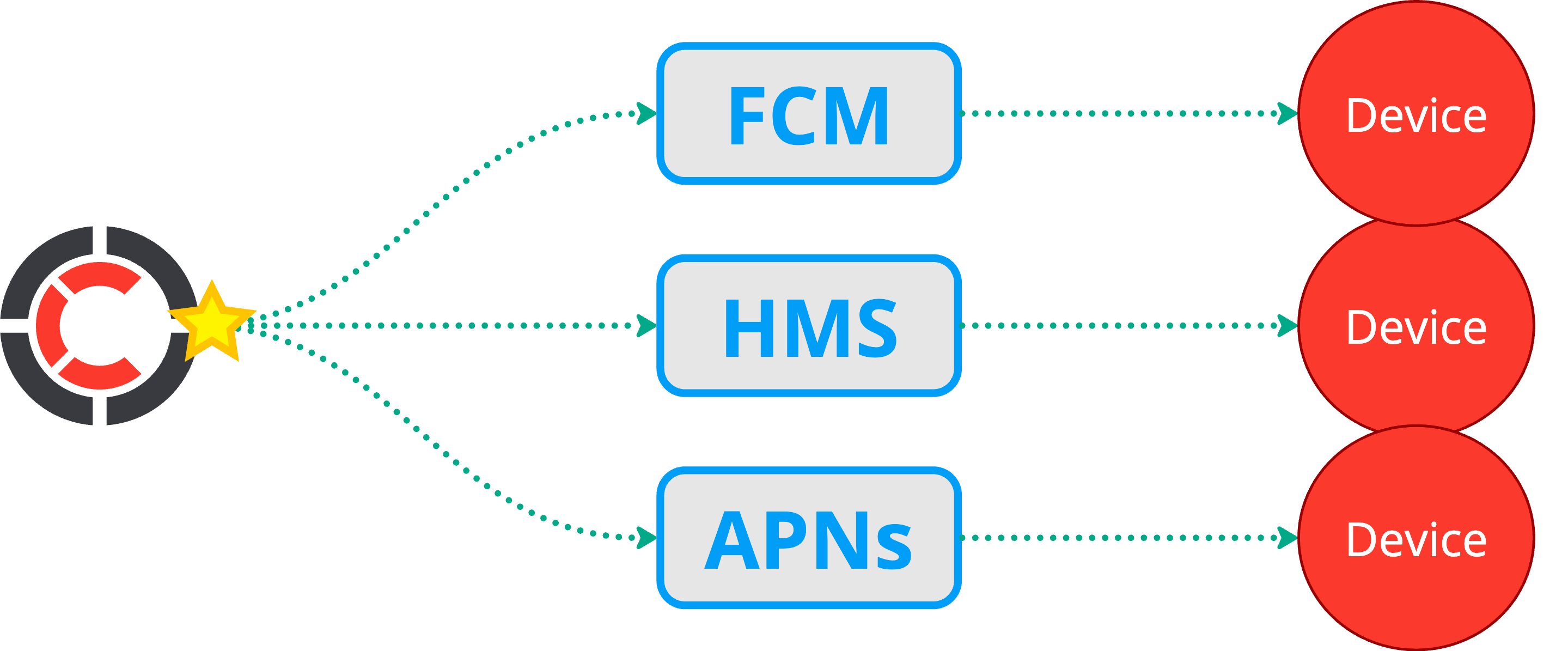
To deliver push notifications to devices Centrifugo PRO integrates with the following providers:
- Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM)
- Huawei Messaging Service (HMS) Push Kit
- Apple Push Notification service (APNs)
FCM, HMS, APNs handle the frontend and transport aspects of notification delivery. Device token storage, management and efficient push notification broadcasting is managed by Centrifugo PRO. Tokens are stored in a PostgreSQL database. To facilitate efficient push notification broadcasting towards devices, Centrifugo PRO includes worker queues based on Redis streams (and also provides an option to use PostgreSQL-based queue).
Integration with FCM means that you can use existing Firebase messaging SDKs to extract push notification token for a device on different platforms (iOS, Android, Flutter, web browser) and setting up push notification listeners. The same for HMS and APNs - just use existing native SDKs and best practices on the frontend. Only a couple of additional steps required to integrate frontend with Centrifugo PRO device token and device topic storage. After doing that you will be able to send push notification towards single device, or towards group of devices subscribed to a topic. For example, with a simple Centrifugo API call like this:
curl -X POST http://localhost:8000/api/send_push_notification \
-H "Authorization: apikey <KEY>" \
-d @- <<'EOF'
{
"recipient": {
"filter": {
"topics": ["test"]
}
},
"notification": {
"fcm": {
"message": {
"notification": {"title": "Hello", "body": "How are you?"}
}
}
}
}
EOF
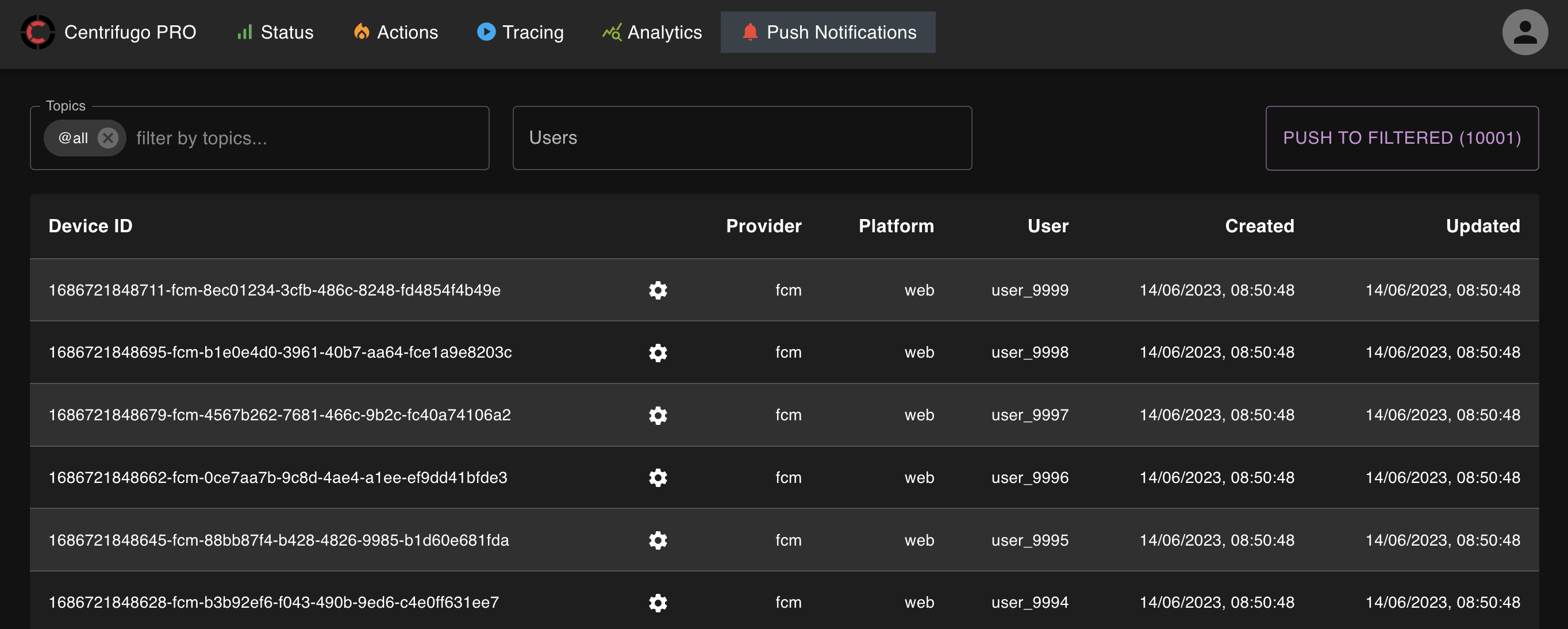
In addition, Centrifugo PRO includes a helpful web UI for inspecting registered devices and sending push notifications:
Motivation and design choices
Centrifugo PRO tries to be practical with its Push Notification API, let's look at its design choices and implementation properties.
Storage for tokens
To start delivering push notifications in the application, developers usually need to integrate with providers such as FCM, HMS, and APNs. This integration typically requires the storage of device tokens in the application database and the implementation of sending push messages to provider push services.
Centrifugo PRO simplifies the process by providing a backend for device token storage, following best practices in token management. It reacts to errors and periodically removes stale devices/tokens to maintain a working set of device tokens based on provider recommendations.
Efficient queuing
Additionally, Centrifugo PRO provides an efficient, scalable queuing mechanism for sending push notifications. Developers can send notifications from the app backend to Centrifugo API with minimal latency and let Centrifugo process sending to FCM, HMS, APNs concurrently using built-in workers. In our tests, we achieved several millions pushes per minute.
Centrifugo PRO also supports delayed push notifications feature – to queue push for a later delivery, so for example you can send notification based on user time zone and let Centrifugo PRO send it when needed.
Unified secure topics
FCM and HMS have a built-in way of sending notification to large groups of devices over topics mechanism (the same for HMS). Topics are great since you can create segments and groups of devices and target specific ones with your notifications.
One problem with native FCM or HMS topics though is that client can subscribe to any topic from the frontend side without any permission check. In today's world this is usually not desired. So Centrifugo PRO re-implements FCM, HMS topics by introducing an additional API to manage device subscriptions to topics.
In some cases you may have real-time channels and device subscription topics with matching names – to send messages to both online and offline users. Though it's up to you.
Centrifugo PRO device topic subscriptions also add a way to introduce the missing topic semantics for APNs.
Centrifugo PRO additionally provides an API to create persistent bindings of user to notification topics. Then – as soon as user registers a device – it will be automatically subscribed to its own topics. As soon as user logs out from the app and you update user ID of the device - user topics bound to the device automatically removed/switched. This design solves one of the issues with FCM – if two different users use the same device it's becoming problematic to unsubscribe the device from large number of topics upon logout. Also, as soon as user to topic binding added (using user_topic_update API) – it will be synchronized across all user active devices. You can still manage such persistent subscriptions on the application backend side if you prefer and provide the full list inside device_register call.
Push personalization
Centrifugo PRO provides several ways to make push notifications individual and take care about better user experience with notifications. This includes:
- Timezone-aware push notifications
- Notification templating
- Notification localizations
- Per user device rate limiting
All these features may be used on individual request basis.
Non-obtrusive proxying
Unlike other solutions that combine different provider push sending APIs into a unified API, Centrifugo PRO provides a non-obtrusive proxy for all the mentioned providers. Developers can send notification payloads in a format defined by each provider.
It's also possible to send notifications into native FCM, HMS topics or send to raw FCM, HMS, APNs tokens using Centrifugo PRO's push API, allowing them to combine native provider primitives with those added by Centrifugo (i.e., sending to a list of device IDs or to a list of topics).
Builtin analytics
Furthermore, Centrifugo PRO offers the ability to inspect sent push notifications using ClickHouse analytics. Providers may also offer their own analytics, such as FCM, which provides insight into push notification delivery. Centrifugo PRO also offers a way to analyze push notification delivery and interaction using the update_push_status API.
Steps to integrate
- Add provider SDK on the frontend side, follow provider instructions for your platform to obtain a push token for a device. For example, for FCM see instructions for iOS, Android, Flutter, Web Browser). The same for HMS or APNs – frontend part should be handled by their native SDKs.
- Call Centrifugo PRO backend API with the obtained token. From the application backend call Centrifugo
device_registerAPI to register the device in Centrifugo PRO storage. Optionally provide list of topics to subscribe device to. - Centrifugo returns a registered device object. Pass a generated device ID to the frontend and save it on the frontend together with a token received from FCM.
- Call Centrifugo
send_push_notificationAPI whenever it's time to deliver a push notification.
At any moment you can inspect device storage by calling device_list API.
Once user logs out from the app, you can detach user ID from device by using device_update or remove device with device_remove API.
Configuration
In Centrifugo PRO you can configure one push provider or use all of them – this choice is up to you.
Enabling push notifications
To enable push notifications, set push_notifications.enabled to true and specify which providers to use in push_notifications.enabled_providers list.
FCM
As mentioned above, Centrifugo uses PostgreSQL for token storage. To enable push notifications make sure database section defined in the configuration and fcm is in the push_notifications.enabled_providers list. Centrifugo PRO uses Redis Streams (default) or PostgreSQL for queuing push notification requests. Finally, to integrate with FCM a path to the credentials file must be provided (see how to create one in this instruction). So the full configuration to start sending push notifications over FCM may look like this:
{
"database": {
"enabled": true,
"postgresql": {
"dsn": "postgresql://postgres:pass@127.0.0.1:5432/postgres"
}
},
"push_notifications": {
"enabled": true,
"queue": {
"redis": {
"address": "localhost:6379"
}
},
"enabled_providers": [
"fcm"
],
"fcm": {
"credentials_file": "/path/to/service/account/credentials.json"
}
}
}
Actually, PostgreSQL database configuration is optional here – you can use push notifications API without it. In this case you will be able to send notifications to FCM, HMS, APNs raw tokens, FCM and HMS native topics and conditions. I.e. using Centrifugo as an efficient proxy for push notifications (for example if you already keep tokens in your database). But sending to device ids and topics, and token/topic management APIs won't be available for usage.
HMS
{
"database": {
"enabled": true,
"postgresql": {
"dsn": "postgresql://postgres:pass@127.0.0.1:5432/postgres"
}
},
"push_notifications": {
"enabled": true,
"queue": {
"redis": {
"address": "localhost:6379"
}
},
"enabled_providers": [
"hms"
],
"hms": {
"app_id": "<your_app_id>",
"app_secret": "<your_app_secret>"
}
}
}
See example how to get app id and app secret here.
APNs
{
"database": {
"enabled": true,
"postgresql": {
"dsn": "postgresql://postgres:pass@127.0.0.1:5432/postgres"
}
},
"push_notifications": {
"enabled": true,
"queue": {
"redis": {
"address": "localhost:6379"
}
},
"enabled_providers": [
"apns"
],
"apns": {
"endpoint": "development",
"bundle_id": "com.example.your_app",
"auth_type": "token",
"token_key_file": "/path/to/auth/key/file.p8",
"token_key_id": "<your_key_id>",
"token_team_id": "your_team_id"
}
}
}
Instead of token_key_file, you can provide the key content inline using token_key_pem:
{
"push_notifications": {
"apns": {
"token_key_pem": "-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----\n...\n-----END PRIVATE KEY-----"
}
}
}
We also support auth over p12 certificates (set auth_type to "cert") with the following options:
push_notifications.apns.cert_p12_file- path to .p12 certificate filepush_notifications.apns.cert_p12_b64- base64-encoded .p12 certificate contentpush_notifications.apns.cert_p12_password- password for .p12 certificate
Use PostgreSQL as queue
Centrifugo PRO utilizes Redis Streams as the default queue engine for push notifications. However, it also offers the option to employ PostgreSQL for queuing. Set push_notifications.queue.type to "postgresql":
{
"database": {
"postgresql": {
"dsn": "postgresql://postgres:pass@127.0.0.1:5432/postgres"
},
"enabled": true
},
"push_notifications": {
"enabled": true,
"queue": {
"type": "postgresql",
"postgresql": {
"reuse_from_database": true
}
}
}
}
Queue based on Redis streams is generally more efficient, so if you start with PostgreSQL based queue – you have an option to switch to a more performant implementation later. Though in-flight and currently queued push notifications will be lost during a switch.
You can also use separate PostgreSQL instance for push notification queue, which may be beneficial:
{
...
"push_notifications": {
"enabled": true,
"queue": {
"type": "postgresql",
"postgresql": {
"dsn": "postgresql://postgres:pass@127.0.0.1:5432/push_queue"
}
}
}
}
Configuration reference
This section provides a comprehensive reference for all push notification configuration options.
push_notifications.enabled
Master switch to enable or disable the push notifications feature.
- Type:
bool - Default:
false
push_notifications.enabled_providers
List of push notification providers to enable.
- Type:
array[string] - Valid values:
"fcm","hms","apns"
push_notifications.dry_run
When true, Centrifugo PRO does not send push notifications to providers but prints logs instead. Useful for development.
- Type:
bool - Default:
false
push_notifications.dry_run_latency
When set together with dry_run, adds artificial delay to workers emulating real-world latency.
- Type:
duration - Default:
0s - Example:
"100ms","1s"
push_notifications.max_inactive_device_interval
Maximum time interval to keep a device without updates. Devices inactive longer than this will be automatically removed. Set to 0s (default) to keep devices indefinitely.
- Type:
duration - Default:
0s - Example:
"720h"(30 days)
push_notifications.read_from_replica
When true, Centrifugo will use PostgreSQL replicas for read operations where possible. Requires database.postgresql.replica_dsn to be configured.
- Type:
bool - Default:
false
push_notifications.queue
Queue configuration object. Centrifugo PRO supports Redis Streams (default) or PostgreSQL for push notification queuing.
push_notifications.queue.type
Specifies the queue backend type.
- Type:
string - Valid values:
"redis","postgresql" - Default:
"redis"
push_notifications.queue.redis
Redis queue configuration object. Supports all standard Redis configuration options (address, Sentinel, Cluster, TLS, etc.). See Redis Engine for common Redis options.
| Field | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
address | string | Redis server address, e.g. "localhost:6379" | |
reuse_from_engine | bool | false | Reuse Redis connection from the engine configuration |
consumer_concurrency | int | 64 | Number of concurrent consumer workers processing push notification jobs |
max_stream_length | int64 | 100000 | Maximum length of the Redis Stream. Older entries may be trimmed when limit is reached |
push_notifications.queue.postgresql
PostgreSQL queue configuration object. Supports DSN, replica DSN, and TLS configuration.
| Field | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
dsn | string | PostgreSQL connection string, e.g. "postgresql://user:pass@localhost:5432/dbname" | |
reuse_from_database | bool | false | Reuse PostgreSQL connection from the database configuration |
consumer_concurrency | int | 16 | Number of concurrent consumer workers |
scheduler_consumer_concurrency | int | 16 | Number of concurrent scheduler consumer workers for delayed pushes |
prefix | string | "" | Table name prefix for queue-related tables |
push_notifications.fcm
FCM (Firebase Cloud Messaging) provider configuration object.
| Field | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
credentials_file | string | Required. Path to Firebase service account credentials JSON file | |
tokens_batch_size | int | 500 | Maximum number of tokens in a single batch request to FCM |
push_notifications.hms
HMS (Huawei Messaging Service) provider configuration object.
| Field | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
app_id | string | Required. Your HMS application ID | |
app_secret | string | Required. Your HMS application secret | |
auth_endpoint | string | Custom HMS authentication endpoint. Uses HMS default if not set | |
push_endpoint | string | Custom HMS push endpoint. Uses HMS default if not set | |
tokens_batch_size | int | 1000 | Maximum number of tokens in a single batch request to HMS |
push_notifications.apns
APNs (Apple Push Notification service) provider configuration object.
| Field | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
endpoint | string | "development" | APNs endpoint: "development", "production", or custom https:// URL |
bundle_id | string | Required. iOS application bundle identifier | |
auth_type | string | Required. Authentication method: "token" or "cert" | |
tokens_batch_size | int | 100 | Maximum number of tokens to process in parallel |
Token-based authentication (auth_type: "token", recommended):
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
token_key_file | string | Path to .p8 authentication key file from Apple Developer portal. Mutually exclusive with token_key_pem |
token_key_pem | string | PEM-encoded authentication key content (inline). Mutually exclusive with token_key_file |
token_key_id | string | Required. 10-character Key ID from Apple Developer account |
token_team_id | string | Required. 10-character Team ID from Apple Developer account |
Certificate-based authentication (auth_type: "cert"):
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
cert_p12_file | string | Path to .p12 certificate file. Mutually exclusive with cert_p12_b64 |
cert_p12_b64 | string | Base64-encoded .p12 certificate content. Mutually exclusive with cert_p12_file |
cert_p12_password | string | Password for .p12 certificate (if encrypted) |
Complete configuration example
Here's a comprehensive example showing all providers configured together:
{
"database": {
"enabled": true,
"postgresql": {
"dsn": "postgresql://postgres:pass@127.0.0.1:5432/postgres",
"replica_dsn": [
"postgresql://postgres:pass@replica-host:5432/postgres"
]
}
},
"push_notifications": {
"enabled": true,
"enabled_providers": ["fcm", "hms", "apns"],
"dry_run": false,
"max_inactive_device_interval": "720h",
"read_from_replica": true,
"queue": {
"type": "redis",
"redis": {
"address": "localhost:6379",
"consumer_concurrency": 64,
"max_stream_length": 100000
}
},
"fcm": {
"credentials_file": "/path/to/fcm-credentials.json",
"tokens_batch_size": 500
},
"hms": {
"app_id": "your_app_id",
"app_secret": "your_app_secret",
"tokens_batch_size": 500
},
"apns": {
"endpoint": "production",
"bundle_id": "com.example.app",
"auth_type": "token",
"token_key_file": "/path/to/AuthKey.p8",
"token_key_id": "ABCDE12345",
"token_team_id": "TEAM123456",
"tokens_batch_size": 100
}
}
}
API description
Push notifications of Centrifugo PRO come with a set of additional server API methods.
device_register
Registers or updates device information.
device_register request
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
id | string | No | ID of the device being registered (provide it when updating). |
provider | string | Yes | Provider of the device token (valid choices: fcm, hms, apns). |
token | string | Yes | Push notification token for the device. |
platform | string | Yes | Platform of the device (valid choices: ios, android, web). |
user | string | No | User associated with the device. |
timezone | string | No | Timezone of device user (IANA time zone identifier, ex. Europe/Nicosia). See Timezone aware push |
locale | string | No | Locale of device user. Must be IETF BCP 47 language tag - ex. en-US, fr-CA. See Localizations |
topics | array[string] | No | Device topic subscriptions. This should be a full list which replaces all the topics previously associated with the device. User topics managed by UserTopic model will be automatically attached. |
meta | map[string]string | No | Additional custom metadata for the device |
device_register result
| Field Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
id | string | Yes | The device ID that was registered/updated. |
device_update
Call this method to update device. For example, when user logs out the app and you need to detach user ID from the device.
device_update request
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
ids | array[string] | No | Device ids to filter |
users | array[string] | No | Device users filter |
user_update | DeviceUserUpdate | No | Optional user update object |
timezone_update | DeviceTimezoneUpdate | No | Optional timezone update object |
locale_update | DeviceLocaleUpdate | No | Optional locale update object |
meta_update | DeviceMetaUpdate | No | Optional device meta update object |
topics_update | DeviceTopicsUpdate | No | Optional topics update object |
DeviceUserUpdate:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
user | string | Yes | User to set |
DeviceTimezoneUpdate:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
timezone | string | Yes | Timezone to set |
DeviceLocaleUpdate:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
locale | string | Yes | Locale to set |
DeviceMetaUpdate:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
meta | map[string]string | Yes | Meta to set |
DeviceTopicsUpdate:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
op | string | Yes | Operation to make: add, remove or set |
topics | array[string] | Yes | Topics for the operation |
device_update result
Empty object.
device_remove
Removes device from storage. This may be also called when user logs out the app and you don't need its device token after that.
device_remove request
| Field Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
ids | array[string] | No | A list of device IDs to be removed |
users | array[string] | No | A list of device user IDs to filter devices to remove |
device_remove result
Empty object.
device_list
Returns a paginated list of registered devices according to request filter conditions.
device_list request
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
filter | DeviceFilter | Yes | How to filter results |
cursor | string | No | Cursor for pagination (last device id in previous batch, empty for first page). |
limit | int32 | No | Maximum number of devices to retrieve. |
include_total_count | bool | No | Flag indicating whether to include total count for the current filter. |
include_topics | bool | No | Flag indicating whether to include topics information for each device. |
include_meta | bool | No | Flag indicating whether to include meta information for each device. |
DeviceFilter:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
ids | array[string] | No | List of device IDs to filter results. |
providers | array[string] | No | List of device token providers to filter results. |
platforms | array[string] | No | List of device platforms to filter results. |
users | array[string] | No | List of device users to filter results. |
topics | array[string] | No | List of topics to filter results. |
device_list result
| Field Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
items | array[Device] | Yes | A list of devices |
next_cursor | string | No | Cursor string for retrieving the next page, if not set - then no next page exists |
total_count | integer | No | Total count value (if include_total_count used) |
Device:
| Field Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
id | string | Yes | The device's ID. |
provider | string | Yes | The device's token provider. |
token | string | Yes | The device's token. |
platform | string | Yes | The device's platform. |
user | string | No | The user associated with the device. |
topics | array[string] | No | Only included if include_topics was true |
meta | map[string]string | No | Only included if include_meta was true |
device_topic_update
Manage mapping of device to topics.
device_topic_update request
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
device_id | string | Yes | Device ID. |
op | string | Yes | add or remove or set |
topics | array[string] | No | List of topics. |
device_topic_update result
Empty object.
device_topic_list
List device to topic mapping.
device_topic_list request
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
filter | DeviceTopicFilter | No | List of device IDs to filter results. |
cursor | string | No | Cursor for pagination (last device id in previous batch, empty for first page). |
limit | int32 | No | Maximum number of devices to retrieve. |
include_device | bool | No | Flag indicating whether to include Device information for each object. |
include_total_count | bool | No | Flag indicating whether to include total count info to response. |
DeviceTopicFilter:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
device_ids | array[string] | No | List of device IDs to filter results. |
device_providers | array[string] | No | List of device token providers to filter results. |
device_platforms | array[string] | No | List of device platforms to filter results. |
device_users | array[string] | No | List of device users to filter results. |
topics | array[string] | No | List of topics to filter results. |
topic_prefix | string | No | Topic prefix to filter results. |
device_topic_list result
| Field Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
items | array[DeviceTopic] | Yes | A list of DeviceTopic objects |
next_cursor | string | No | Cursor string for retrieving the next page, if not set - then no next page exists |
total_count | integer | No | Total count value (if include_total_count used) |
DeviceTopic:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
id | string | Yes | ID of DeviceTopic object |
device_id | string | Yes | Device ID |
topic | string | Yes | Topic |
user_topic_update
Manage mapping of topics with users. These user topics will be automatically attached to user devices upon registering. And removed from device upon detaching user.
user_topic_update request
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
user | string | Yes | User ID. |
op | string | Yes | add or remove or set |
topics | array[string] | No | List of topics. |
user_topic_update result
Empty object.
user_topic_list
List user to topic mapping.
user_topic_list request
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
filter | UserTopicFilter | No | Filter object. |
cursor | string | No | Cursor for pagination (last id in previous batch, empty for first page). |
limit | int32 | No | Maximum number of UserTopic objects to retrieve. |
include_total_count | bool | No | Flag indicating whether to include total count info to response. |
UserTopicFilter:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
users | array[string] | No | List of users to filter results. |
topics | array[string] | No | List of topics to filter results. |
topic_prefix | string | No | Topic prefix to filter results. |
user_topic_list result
| Field Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
items | array[UserTopic] | Yes | A list of UserTopic objects |
next_cursor | string | No | Cursor string for retrieving the next page, if not set - then no next page exists |
total_count | integer | No | Total count value (if include_total_count used) |
UserTopic:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
id | string | Yes | ID of UserTopic |
user | string | Yes | User ID |
topic | string | Yes | Topic |
send_push_notification
Send push notification to specific device_ids, or to topics, or native provider identifiers like fcm_tokens, or to fcm_topic. Request will be queued by Centrifugo, consumed by Centrifugo built-in workers and sent to the provider API.
send_push_notification request
| Field name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
recipient | PushRecipient | Yes | Recipient of push notification |
notification | PushNotification | Yes | Push notification to send |
uid | string | No | Unique identifier for each push notification request, can be used to cancel push. We recommend using UUID v4 for it. Two different requests must have different uid |
send_at | int64 | No | Optional Unix time in the future (in seconds) when to send push notification, push will be queued until that time. |
optimize_for_reliability | bool | No | Makes processing heavier, but tolerates edge cases, like not losing inflight pushes due to temporary queue unavailability. |
limit_strategy | PushLimitStrategy | No | Can be used to set push time constraints (based on device timezone) and rate limits. Note, when it's used Centrifugo processes pushes one by one instead of batch sending |
analytics_uid | string | No | Identifier for push notification analytics, if not set - Centrifugo will use uid field. |
localizations | map[string]PushLocalization | No | Optional per language localizations for push notification. |
use_templating | bool | No | If set - Centrifugo will use templating for push notification. Note that setting localizations enables templating automatically. |
use_meta | bool | No | If set - Centrifugo will additionally load device meta during push sending, this meta becomes available in templating. |
PushRecipient (you must set only one of the following fields):
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
filter | DeviceFilter | No | Send to device IDs based on Centrifugo device storage filter |
fcm_tokens | array[string] | No | Send to a list of FCM native tokens |
fcm_topic | string | No | Send to a FCM native topic |
fcm_condition | string | No | Send to a FCM native condition |
hms_tokens | array[string] | No | Send to a list of HMS native tokens |
hms_topic | string | No | Send to a HMS native topic |
hms_condition | string | No | Send to a HMS native condition |
apns_tokens | array[string] | No | Send to a list of APNs native tokens |
PushNotification:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
expire_at | int64 | No | Unix timestamp when Centrifugo stops attempting to send this notification. Note, it's Centrifugo specific and does not relate to notification TTL fields. We generally recommend to always set this to a reasonable value to protect your app from old push notifications sending |
fcm | FcmPushNotification | No | Notification for FCM |
hms | HmsPushNotification | No | Notification for HMS |
apns | ApnsPushNotification | No | Notification for APNs |
FcmPushNotification:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
message | JSON object | Yes | FCM Message described in FCM docs. |
HmsPushNotification:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
message | JSON object | Yes | HMS Message described in HMS Push Kit docs. |
ApnsPushNotification:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
headers | map[string]string | No | APNs headers |
payload | JSON object | Yes | APNs payload |
PushLocalization:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
translations | map[string]string | Yes | Variable name to value for the specific language. |
PushLimitStrategy:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
rate_limit | PushRateLimitStrategy | No | Set rate limit policies |
time_limit | PushTimeLimitStrategy | No | Set time limit policy |
PushRateLimitStrategy:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
key | string | No | Optional key for rate limit policy, supports variables (device.id and device.user). |
policies | array[RateLimitPolicy] | No | Array of rate limit policies to apply |
drop_if_rate_limited | bool | No | Drop push if rate limited, otherwise queue for later |
RateLimitPolicy:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
rate | int | Yes | Allowed rate |
interval_ms | int | Yes | Interval over which rate is allowed |
PushTimeLimitStrategy:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
send_after_time | string | Yes | Local time in format HH:MM:SS after which push must be sent |
send_before_time | string | Yes | Local time in format HH:MM:SS before which push must be sent |
no_tz_send_now | bool | No | If device does not have timezone send push immediately, by default - will be dropped |
send_push_notification result
| Field Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
uid | string | Unique send id, matches uid in request if it was provided |
cancel_push
Cancel delayed push notification (which was sent with custom send_at value).
cancel_push request
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
uid | string | Yes | uid of push notification to cancel |
cancel_push result
Empty object.
update_push_status
This API call is experimental, some changes may happen here.
Centrifugo PRO also allows tracking status of push notification delivery and interaction. It's possible to use update_push_status API to save the updated status of push notification to the notifications analytics table. Then it's possible to build insights into push notification effectiveness by querying the table.
The update_push_status API supposes that you are using uid field with each notification sent and you are using Centrifugo PRO generated device IDs (as described in steps to integrate).
This is a part of server API at the moment, so you need to proxy requests to this endpoint over your backend. We can consider making this API suitable for requests from the client side – please reach out if your use case requires it.
update_push_status request
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
analytics_uid | string | Yes | analytics_uid from send_push_notification |
status | string | Yes | Status of push notification - delivered or interacted |
device_id | string | Yes | Device ID |
msg_id | string | No | Optional Message ID of push notification issued by the provider |
update_push_status result
Empty object.
Timezone aware push
Setting timezone to a device (see device_register call) opens a road for timezone-aware push notifications. This is nice because you can send notifications to users in a convenient time of the day. Avoid pushes at night, push at specific time.
To send such push notifications use time_limit field of PushLimitStrategy. For example, you can send push between 09:00:00 and 09:30:00 – and Centrifugo will send push somewhere during this period of user's local time.
Given Centrifugo takes timezone from devices table into account timezone aware pushes only work with requests where DeviceFilter is used for sending – i.e. when Centrifugo iterates over devices in the database. If you send using raw tokens and want to inherit possibility to use timezones - reach out to us, this may be supported.
Templating
It's possible to use templating in the content of your push notifications payloads. By default, Centrifugo does not use templating since this allows broadcasting pushes at max speed. You have to set use_templating flag to true when sending push to enable template execution. Here is an example of using templating:
{
..
"title": "Hello {{.device.meta.first_name}}"
To access device meta content in push template (as shown above) additionally set use_meta flag to true in send push notification request. Without use_meta you only have access to .device.id and .device.user variables.
Templating only works with requests where DeviceFilter is used for sending – i.e. when Centrifugo iterates over devices in the database.
Localizations
Templating also allows us to localize push notification content based on device locale (see device_register call).
When sending push notification use localizations field of send_push_notification request:
{
..
"localizations": {
"pt": {
"translations": {
"greeting": "Olá",
"question": "Como tá indo"
}
},
"fr": {
"translations": {
"greeting": "Bonjour",
"question": "Comment ça va"
}
}
}
}
In push payload you can then use templating and l10n object will be set to a proper translation map based on device locale:
{
..
"title": "{{default [[hello]] .l10n.greeting}}! {{ default [[How is it going]] .l10n.question }} ?"
So that a device with pt-BR locale will get a push notification with title Olá! Como tá indo?.
Note, it's required to set default value here (we used English language in the example) for the cases when no locale found in device, or no translations for the device language provided in the request.
Push rate limits
A good practice when working with push notifications is to avoid sending too many notifications to your users, especially marketing ones. Centrifugo PRO provides a way to rate limit notifications on user's device level.
To do this, use rate_limit field of PushLimitStrategy. For example, you can configure policies to send push notifications not faster than once per minute and not more pushes than 10 in one hour. I.e. Centrifugo supports several policies for rate limit strategy. If push notification hits provided rate limits then it will be automatically delayed, or dropped if drop_if_rate_limited flag set to true.
Given Centrifugo takes timezone from devices table into account timezone aware pushes only work with requests where DeviceFilter is used for sending – i.e. when Centrifugo iterates over devices in the database. If you send using raw tokens and want to inherit possibility to use rate limits - reach out to us, this may be supported.
Exposed metrics
Several metrics are available to monitor the state of Centrifugo push worker system:
centrifugo_push_notification_count
- Type: Counter
- Labels: provider, recipient_type, platform, success, err_code
- Description: Total count of push notifications.
- Usage: Helps in tracking the number and success rate of push notifications sent, providing insights for optimization and troubleshooting.
centrifugo_push_queue_consuming_lag
- Type: Gauge
- Labels: provider, queue
- Description: Queue consuming lag in seconds.
- Usage: Useful for monitoring the delay in processing jobs from the queue, helping identify potential bottlenecks and ensuring timely processing.
centrifugo_push_consuming_inflight_jobs
- Type: Gauge
- Labels: provider, queue
- Description: Number of inflight jobs being consumed.
- Usage: Helps in tracking the load on the job processing system, ensuring that resources are being utilized efficiently.
centrifugo_push_job_duration_seconds
- Type: Summary
- Labels: provider, recipient_type
- Description: Duration of push processing job in seconds.
- Usage: Useful for monitoring the performance of job processing, helping in performance tuning and issue resolution.
Further reading and tutorials
Some additional materials include:
- Blog post Discovering Centrifugo PRO: push notifications API
- Adding push notifications to our Grand Messenger Tutorial