Server observability
To provide a better server observability Centrifugo supports reporting metrics in Prometheus format and can automatically export metrics to Graphite.
Metrics
Prometheus metrics
To enable Prometheus endpoint start Centrifugo with prometheus option on:
{
"prometheus": {
"enabled": true
}
}
This will enable /metrics endpoint so the Centrifugo instance can be monitored by your Prometheus server.
Graphite metrics
To enable automatic export to Graphite (via TCP):
{
"graphite": {
"enabled": true,
"host": "localhost",
"port": 2003
}
}
By default, stats will be aggregated over 10 seconds intervals inside Centrifugo and then pushed to Graphite over TCP connection.
If you need to change this aggregation interval use the graphite_interval option (in seconds, default 10).
Grafana dashboard
Check out Centrifugo official Grafana dashboard for Prometheus storage. You can import that dashboard to your Grafana, point to Prometheus storage – and enjoy visualized metrics.
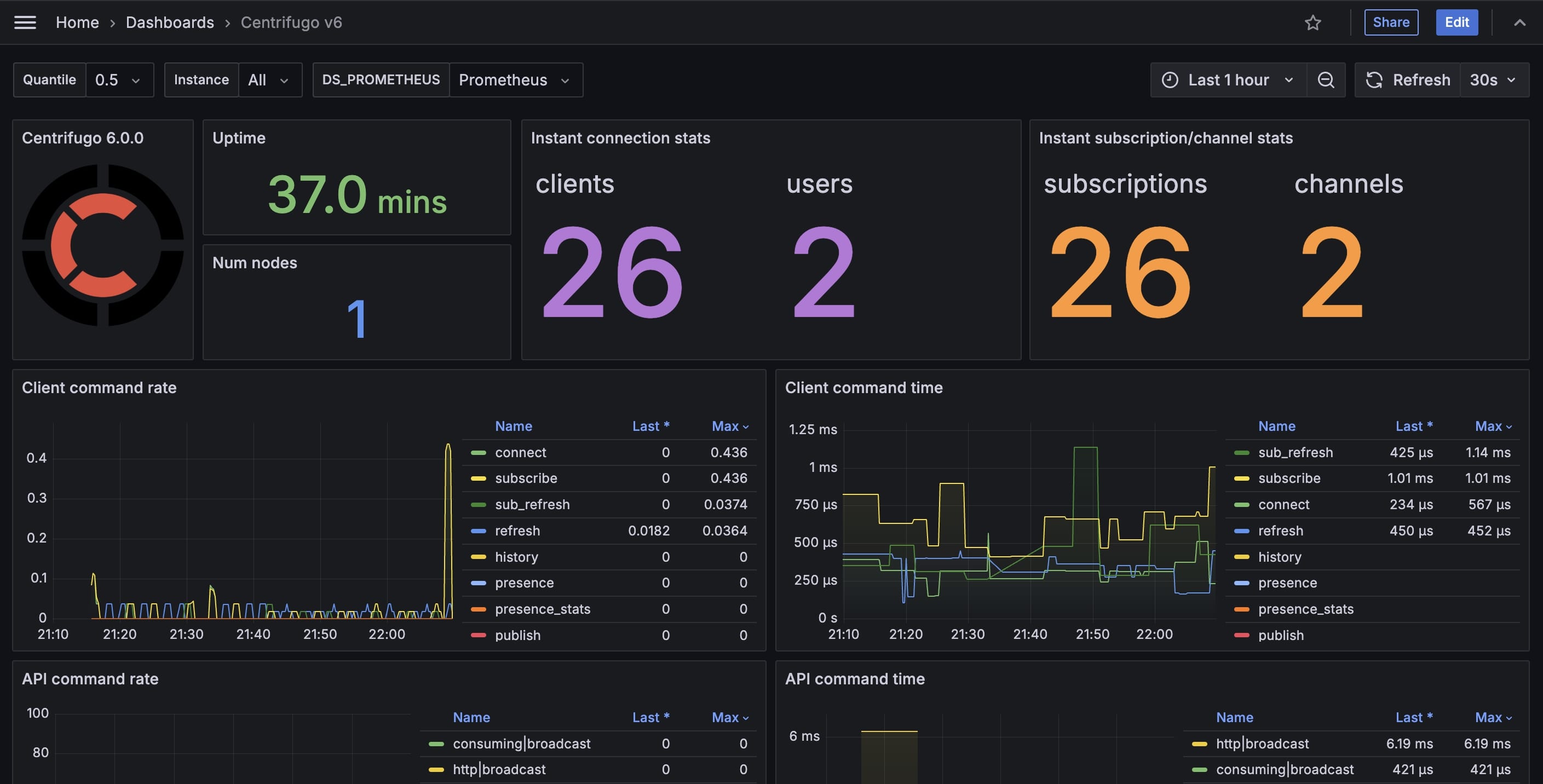
Exposed metrics
Here is a description of various metrics exposed by Centrifugo.
centrifugo_node_messages_sent_count
- Type: Counter
- Labels: type, channel_namespace (Centrifugo PRO)
- Description: Tracks the number of messages sent by a node to the broker.
- Usage: Use this metric to monitor the outgoing message rate and detect any anomalies or spikes in the data flow.
centrifugo_node_messages_received_count
- Type: Counter
- Labels: type, channel_namespace (Centrifugo PRO)
- Description: Measures the number of messages received from the broker.
- Usage: Helps in understanding the incoming message rate and ensures the node is receiving data as expected.
centrifugo_node_action_count
- Type: Counter
- Labels: action, channel_namespace (Centrifugo PRO)
- Description: Counts the number of various actions called within the node.
- Usage: Useful for tracking specific actions' usage and frequency.
centrifugo_node_num_clients
- Type: Gauge
- Description: Shows the current number of clients connected to the node.
- Usage: Monitor the client connections to ensure the node is not reaching its capacity.
centrifugo_node_num_users
- Type: Gauge
- Description: Displays the number of unique users connected to the node.
- Usage: Helps in understanding user engagement and capacity planning.
centrifugo_node_num_subscriptions
- Type: Gauge
- Description: Indicates the number of active subscriptions.
- Usage: Use this to monitor the subscription levels and identify any potential issues or required optimizations.
centrifugo_node_num_nodes
- Type: Gauge
- Description: Shows the total number of nodes in the cluster.
- Usage: Essential for monitoring the size of the cluster and ensuring that all nodes are operational.
centrifugo_node_build
- Type: Gauge
- Labels: version
- Description: Provides build information of the node.
- Usage: Helps in tracking the version of the application running across different environments.
centrifugo_node_num_channels
- Type: Gauge
- Description: Counts the number of channels with one or more subscribers.
- Usage: Useful for monitoring the activity and utilization of channels.
centrifugo_node_survey_duration_seconds
- Type: Summary
- Labels: op
- Description: Captures the duration of surveys conducted by the node.
- Usage: Helps in performance monitoring and identifying any delays or issues in survey operations.
centrifugo_client_num_reply_errors
- Type: Counter
- Labels: method, code, channel_namespace (Centrifugo PRO)
- Description: Counts the number of errors in replies sent to clients.
- Usage: Critical for error monitoring and ensuring smooth client interactions.
centrifugo_client_num_server_unsubscribes
- Type: Counter
- Labels: code, channel_namespace (Centrifugo PRO)
- Description: Tracks the number of server-initiated unsubscribes.
- Usage: Use this to monitor the health of client connections and identify potential issues with the server.
centrifugo_client_num_server_disconnects
- Type: Counter
- Labels: code
- Description: Tracks the number of server-initiated disconnects.
- Usage: Use this to monitor the health of client connections and identify potential issues with the server.
centrifugo_client_command_duration_seconds
- Type: Summary
- Labels: method, channel_namespace (Centrifugo PRO)
- Description: Measures the duration of commands executed by clients.
- Usage: Essential for performance monitoring and ensuring timely responses to client commands.
centrifugo_client_recover
- Type: Counter
- Labels: recovered, channel_namespace (Centrifugo PRO), has_recovered_publications
- Description: Counts the number of recover operations performed.
- Usage: Helps in tracking the system's resilience and recovery mechanisms. Label
recovered- was recovery successful or not. Labelhas_recovered_publications- did successful recovery contain some publications or no publications were missed by a client.
centrifugo_client_recovered_publications
New in Centrifugo v6.2.4
Note, this metric is disabled by default. To enable it set prometheus.recovered_publications_histogram option to true in the configuration file.
{
"prometheus": {
"recovered_publications_histogram": true
}
}
- Type: Histogram
- Labels: channel_namespace
- Description: Measures the number of publications recovered by clients.
- Usage: Use this metric to monitor the effectiveness of the recovery process.
centrifugo_client_connection_limit_reached_total
- Type: Counter
- Labels: None
- Description: Number of refused connections due to the node client connection limit.
- Usage: Useful for monitoring the load on the Centrifugo node and identifying when clients are being refused connections due to reaching the connection limit.
centrifugo_client_connections_accepted
- Type: Counter
- Labels: transport, accept_protocol (Centrifugo PRO), client_name, client_version
- Description: Count of accepted client connections by transport type, protocol, client name, and version.
- Usage: Helps in tracking connection patterns, understanding which clients and transports are being used, and monitoring client version distribution across your infrastructure.
centrifugo_client_connections_inflight
- Type: Gauge
- Labels: transport, accept_protocol (Centrifugo PRO), client_name, client_version
- Description: Number of currently active client connections by transport type, protocol, client name, and version.
- Usage: Useful for real-time monitoring of active connections, understanding the current load distribution across different transports and client types, and capacity planning.
centrifugo_client_subscriptions_accepted
- Type: Counter
- Labels: client_name, channel_namespace (Centrifugo PRO)
- Description: Count of accepted client subscriptions by client name and channel namespace.
- Usage: Useful for monitoring subscription patterns, understanding which clients are subscribing to which channel namespaces, and tracking subscription volume over time.
centrifugo_client_subscriptions_inflight
- Type: Gauge
- Labels: client_name, channel_namespace (Centrifugo PRO)
- Description: Number of currently active client subscriptions by client name and channel namespace.
- Usage: Essential for real-time monitoring of active subscriptions, understanding which clients and channel namespaces have the most active subscriptions, and capacity planning for subscription load.
centrifugo_client_ping_pong_duration_seconds
- Type: Histogram
- Labels: transport
- Description: Tracks the duration of ping/pong – i.e. time between sending ping to client and receiving pong from client.
- Usage: Helps in monitoring the client protocol performance, latency, making sure frame processing does not take too much time on the client side.
centrifugo_transport_messages_sent
- Type: Counter
- Labels: transport, frame_type, channel_namespace
- Description: Tracks the number of messages sent to client connections over specific transports.
- Usage: Essential for understanding the data flow and performance of different transports.
centrifugo_transport_messages_sent_size
- Type: Counter
- Labels: transport, frame_type, channel_namespace
- Description: Measures the size of messages (in bytes) sent to client connections over specific transports.
- Usage: Helps in monitoring the network bandwidth usage and optimizing the data transfer.
centrifugo_transport_messages_received
- Type: Counter
- Labels: transport, frame_type, channel_namespace
- Description: Counts the number of messages received from client connections over specific transports.
- Usage: Important for ensuring that messages are being successfully received and processed.
centrifugo_transport_messages_received_size
- Type: Counter
- Labels: transport, frame_type, channel_namespace
- Description: Measures the size of messages (in bytes) received from client connections over specific transports.
- Usage: Use this metric to monitor the incoming data size and optimize the application's performance.
centrifugo_proxy_duration_seconds
- Type: Summary & Histogram
- Labels: protocol, type
- Description: Captures the duration of proxy calls.
- Usage: Critical for understanding the performance of proxy calls and identifying any potential bottlenecks or issues.
centrifugo_proxy_errors
- Type: Counter
- Labels: protocol, type
- Description: Counts the number of errors occurred during proxy calls.
- Usage: Helps in monitoring the reliability of proxy services and ensuring error-free operations.
centrifugo_granular_proxy_duration_seconds
- Type: Summary & Histogram
- Labels: type, name
- Description: Measures the duration of granular proxy calls.
- Usage: Use this to get more detailed insights into the performance of granular proxy operations.
centrifugo_granular_proxy_errors
- Type: Counter
- Labels: type, name
- Description: Counts the number of errors in granular proxy calls.
- Usage: Essential for error tracking and ensuring the stability of granular proxy services.
centrifugo_api_command_duration_seconds
- Type: Summary
- Labels: protocol, method
- Description: Tracks the duration of API commands.
- Usage: Helps in monitoring the API performance and ensuring timely responses.
centrifugo_api_command_duration_seconds_histogram
- Type: Histogram
- Labels: protocol, method
- Description: Tracks the duration of API commands.
- Usage: Helps in monitoring the API performance and ensuring timely responses.
centrifugo_node_pub_sub_lag_seconds
- Type: Histogram
- Labels:
- Description: Tracks pub sub lag in seconds.
- Usage: Helps in monitoring of PUB/SUB layer performance. Note, this metric may be not exact in distributed environment due to time skew (to minify effect use NTP). In this case it still may be useful to identifies growth in lag.
centrifugo_node_broadcast_duration_seconds
- Type: Histogram
- Labels: type, channel_namespace (Centrifugo PRO)
- Description: Tracks broadcast duration in seconds.
- Usage: Useful to monitor time required for broadcasting the message to subscribers on the node. If it grows and the number of messages increases – may indicate the need to scale.
centrifugo_node_tags_filter_dropped_publications
- Type: Counter
- Labels: channel_namespace (Centrifugo PRO)
- Description: Counts the number of publications dropped due to tags filtering.
- Usage: Helps in monitoring the effectiveness of tags filtering and identifying any potential issues.
centrifugo_broker_redis_pub_sub_errors
- Type: Counter
- Labels: broker_name, error
- Description: Number of times there was an error in Redis PUB/SUB connection.
- Usage: Critical for monitoring Redis broker health and identifying connection issues that could affect message delivery.
centrifugo_broker_redis_pub_sub_dropped_messages
- Type: Counter
- Labels: broker_name, channel_type
- Description: Number of dropped messages on application level in Redis PUB/SUB.
- Usage: Helps identify message loss issues in the Redis broker, which could indicate performance problems or buffer overflows.
centrifugo_broker_redis_pub_sub_buffered_messages
- Type: Gauge
- Labels: broker_name, channel_type, pub_sub_processor
- Description: Number of messages buffered in Redis PUB/SUB.
- Usage: Monitor buffer levels to detect potential bottlenecks in message processing and prevent message drops.
Traces
OpenTelemetry
At this point Centrifugo can export traces for HTTP and GRPC server API requests in OpenTelemetry format.
To enable:
{
"opentelemetry": {
"enabled": true,
"api": true
}
}
OpenTelemetry must be explicitly turned on to avoid tracing overhead when it's not needed.
To configure OpenTelemetry export behaviour we are relying on OpenTelemetry environment vars supporting only HTTP export endpoints for now.
So a simple example to run Centrifugo with server API tracing would be running Jaeger with COLLECTOR_OTLP_ENABLED:
docker run --rm -it --name jaeger \
-e COLLECTOR_OTLP_ENABLED=true \
-p 16686:16686 \
-p 4318:4318 \
jaegertracing/all-in-one:latest
Then start Centrifugo:
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT="http://localhost:4318" CENTRIFUGO_OPENTELEMETRY=1 CENTRIFUGO_OPENTELEMETRY_API=1 ./centrifugo
Send some API requests - and open http://localhost:16686 to see traces in Jaeger UI.
By default, Centrifugo exports traces in http/protobuf format. If you want to use GRPC exporter then it's possible to turn it on by setting environment variable OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_PROTOCOL to grpc (GRPC exporter format supported since Centrifugo v5.0.3).
Logs
Logging may be configured using log_level option. It may have the following values:
nonetracedebuginfo(default)warnerror
We generally do not recommend anything below info to be used in production.
By default, Centrifugo logs to STDOUT. Usually this is what you need when running servers on modern infrastructures. Logging into file may be configured using log_file option.